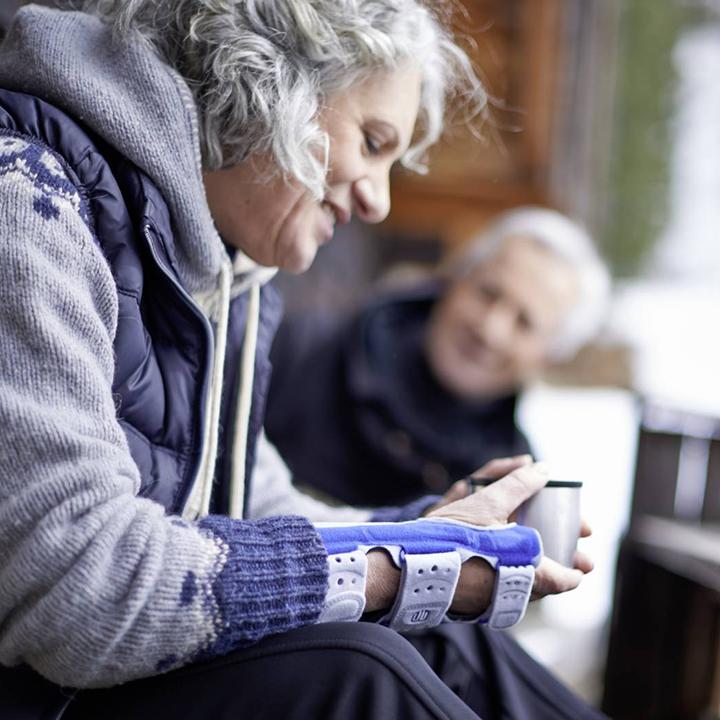
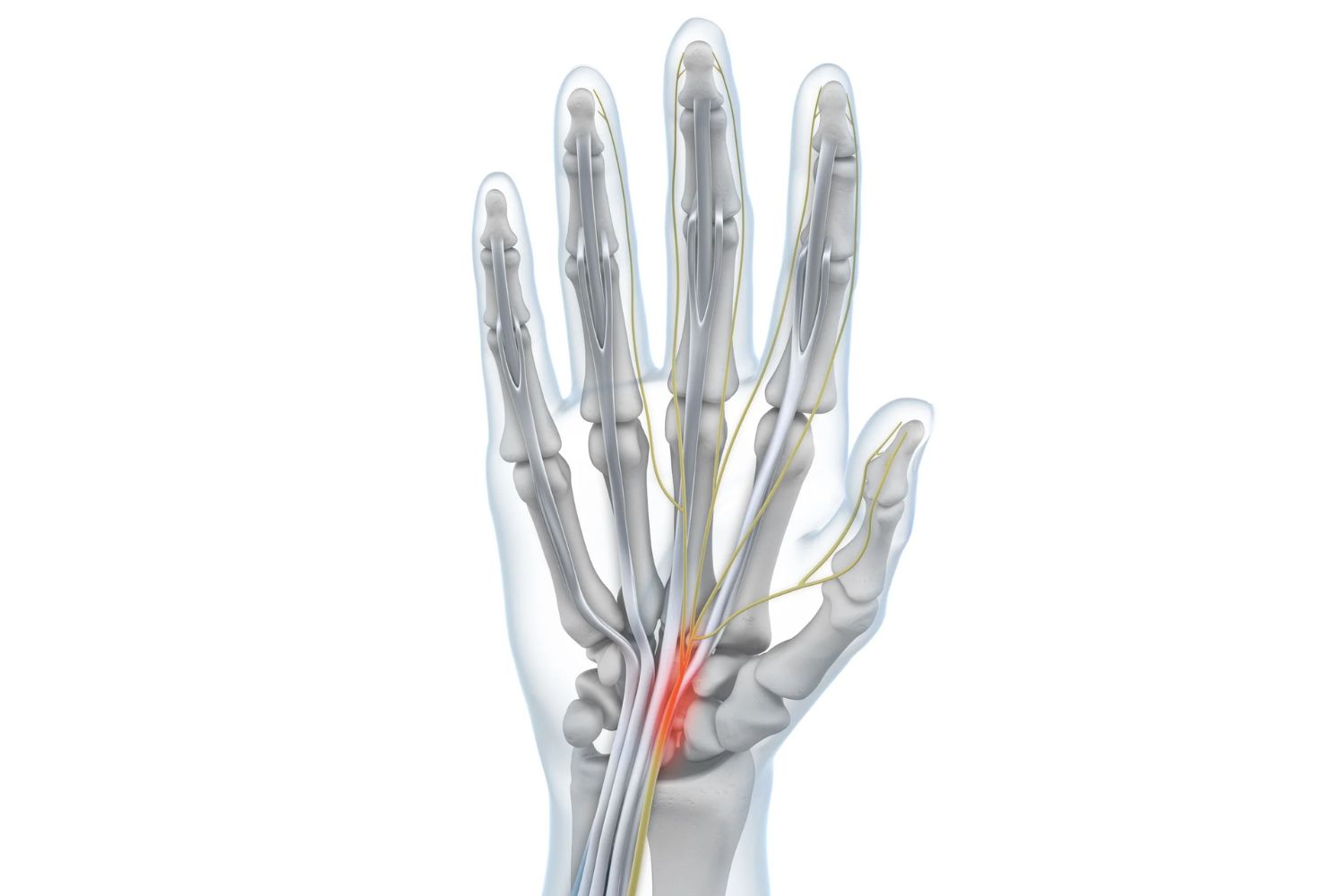
Uneven or excessive pressure exerted by the wrist joint on the nerves in the hand can lead to tingling and a numb sensation in the hand and arms. This condition is called Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
Mild cases of carpal tunnel syndrome usually resolve by themselves; however, if untreated, the condition often grows progressively worse and can lead to long-term degeneration, including pain and rigidity.
In chronic cases, the patient experiences intense pain and stiffness in the hand and arms. The joint mobility is severely impacted, which can have debilitating effects on a patient’s quality of life.
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when uneven or excessive pressure is applied to the median nerve. The tunnel that holds the nerves and blood vessels is constricted, leading to a build-up of pressure. Some of the more common factors that lead to the development of this condition include:
- Malformations in the wrist and an innate narrowness of the carpal tunnel from birth.
- Inflammation and swelling of the surrounding soft tissue that leads to sustained pressure.
- Frequent and repeated movements that lead to overstraining of the wrist. For example, typing at a keyboard all day, writing with a pen/pencil for extended periods, and domestic work like cleaning/washing.
- Accidental trauma or injury to the forearm, wrist or hand.
- Obesity, diabetes, or thyroid disorders could lead to fluid buildup in the soft tissue, which in turn increases pressure on the median nerve.
- Presence of a growth or tumour in the Carpal Tunnel.
- Hormonal changes can cause the inner skin of the joint to swell. This is especially common in women during pregnancy.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Symptoms
Some of the more common symptoms of Carpal tunnel syndrome include:
- Tingling and numbness in the hands and arms.
- Initially, symptoms of pain and discomfort show up during strenuous activities and after long periods of inactivity, such as a long night’s sleep.
- A recurring sensation of hands “falling asleep”.
- In chronic cases, the joint becomes stiff and mobility is severely restricted.
Reduced functioning and permanent paralysis are fairly significant risks due to degeneration, and it is highly advised that patients seek immediate medical attention if they experience symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome. Early treatment is essential to prevent such issues from occurring.
Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
A medical professional begins with a complete patient history and a physical examination of the elbow. This provides critical information about the patient's risk factors and allows for a study of the condition's progression.
Functional and provocation tests measure the median nerve conduction speed and can be conducted by a GP.
Sophisticated imaging technology, such as X-rays and Ultrasound, can provide more information about the joint's spatial conditions.
Treatment for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
Treatment for Carpal Tunnel syndrome depends entirely on the progression of the disease. Providing ample support and stabilisation to the joint can help treat any damage done to the wrist. Early intervention is the best course of action to prevent degeneration and permanent nerve damage.
Immobilisation
Immobilising the wrist through the night and preferably through the day has proven effective in managing the symptoms of the condition. This is best done with a brace. This allows the wrist to rest and heal quickly.
- Rehabilitation And Physiotherapy.
- Regular physiotherapy helps with targeted muscle training and is a proven effective treatment path. The physiotherapy exercises can help promote muscle reorganisation and are the most effective option to curb the disease.
- Encouraging healthy proprioception and strengthening of the muscles in the wrist helps prevent long-term degeneration.
- Regular targeted exercises, as instructed by a doctor or physiotherapist, are highly recommended to help maintain joint mobility and effective functioning.
- Prescribed Painkillers.
Painkillers such as Ibuprofen or Panadol can help alleviate pain and discomfort in patients. Pain, however, is a crucial indicator of injury. Painkillers merely mask the pain without addressing the underlying condition. They should only be used when directed by a doctor and not for extended periods.
Wrist Brace and Support
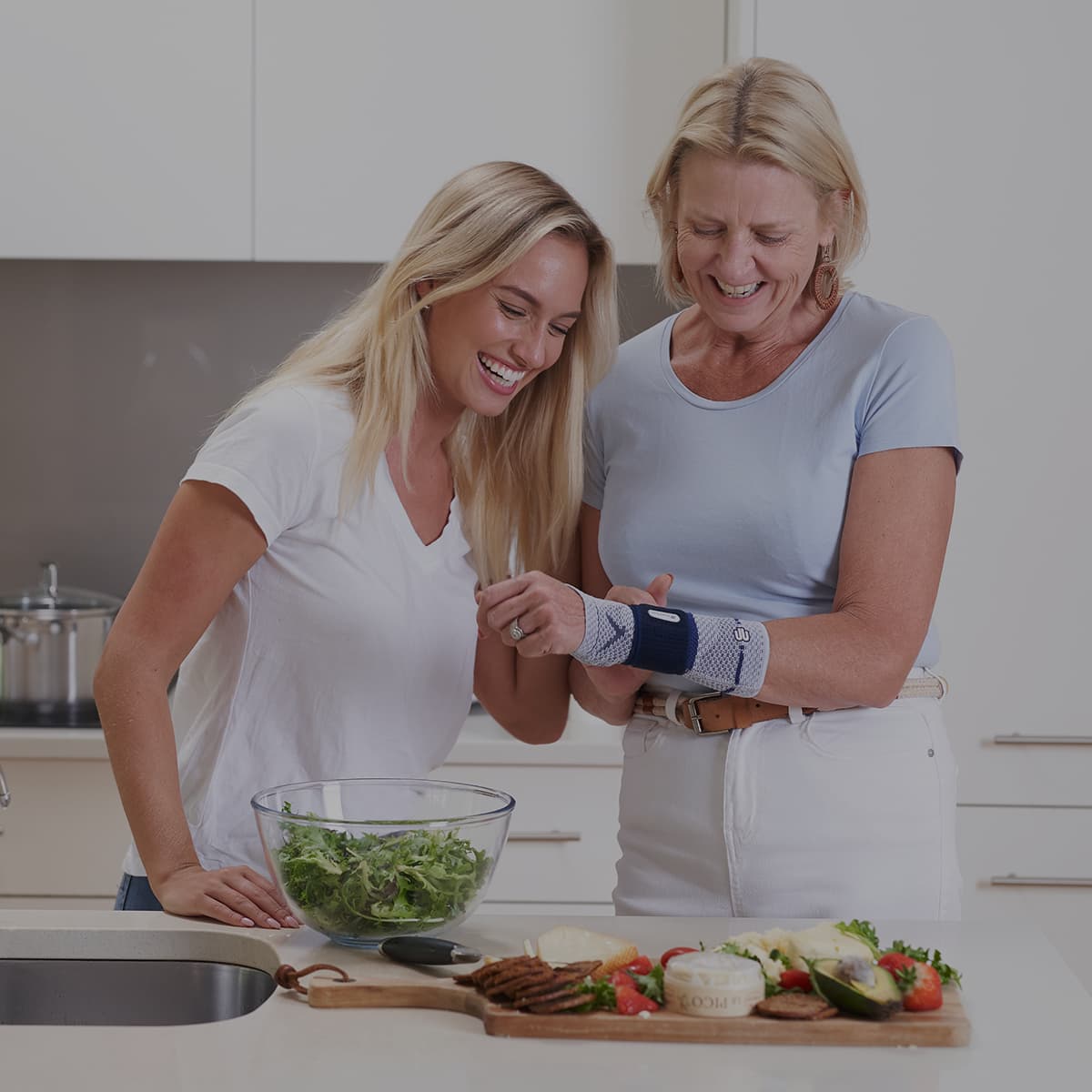
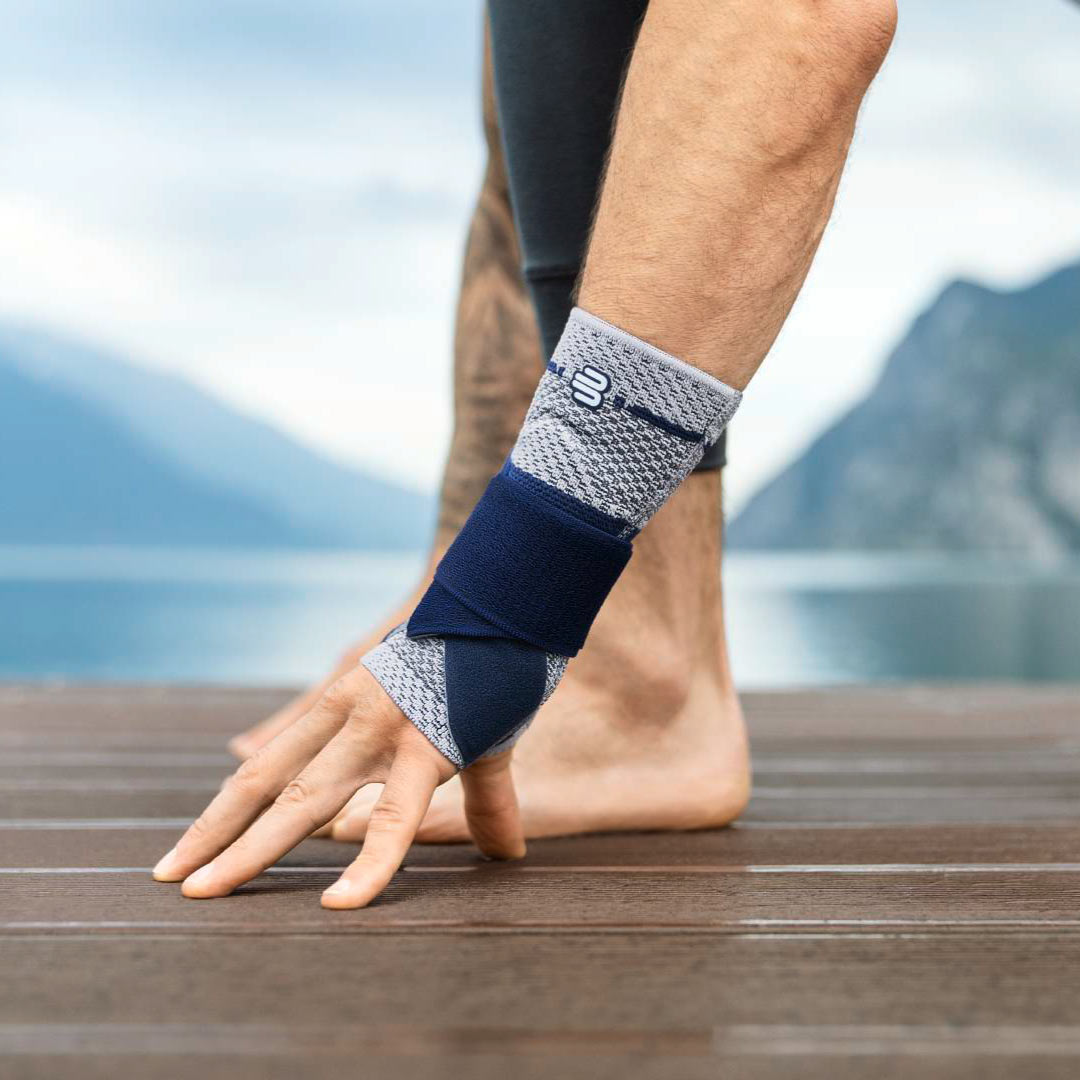
A medical wrist brace or splint will help reduce the pain and discomfort patients experience by taking pressure off the joint. Wearing a Bauerfeind wrist brace like the ManuTrain or ManuLoc helps minimise the chances of injury and deterioration by providing enhanced stability, proprioception, and comfort. This is not found in simple neoprene sleeves and braces and is instrumental in a speedy recovery.
Surgical Intervention
Operative surgery is considered in severe cases where symptoms are persistent, and all conservative treatments have been exhausted. In chronic conditions, a surgeon can perform operative surgery on the carpal ligament surrounding the carpal tunnel.
This also allows the surgeon to clear any constricting tissue and relieve the median nerve. Patients have reported alleviation and, in some cases, elimination of symptoms post-operation. However, this is a last resort and carries with it more risk than any other treatment.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Wrist Braces & Supports
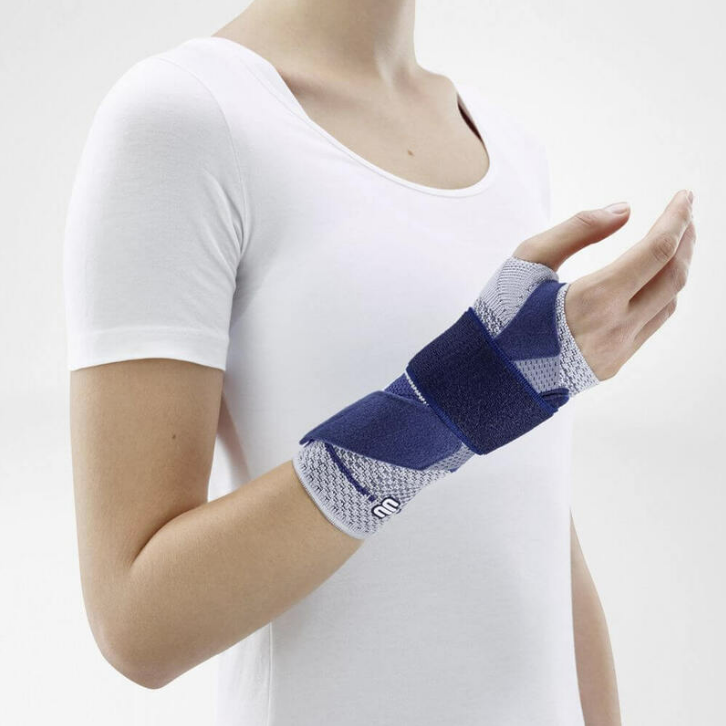
ManuTrain Wrist Support
Medical wrist braces like the ManuTrain and the ManuLoc are perfect for everyday conservative and post-operative care, making them ideal for anyone suffering from Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, regardless of stage.
The ManuTrain Wrist Support features a stay running along the underside of the wrist, which helps provide greater stability to the wrist. This stay can be used to further prevent wrist movement, without full immobilisation. An additional Velcro strap can be used to further enhance the stabilisation and compressive effect of the ManuTrain.
Unlike the ManuLoc, the ManuTrain features two contoured gel massage pads. These gel pads help relieve strain and pressure on the nerves and blood vessels in the wrist.
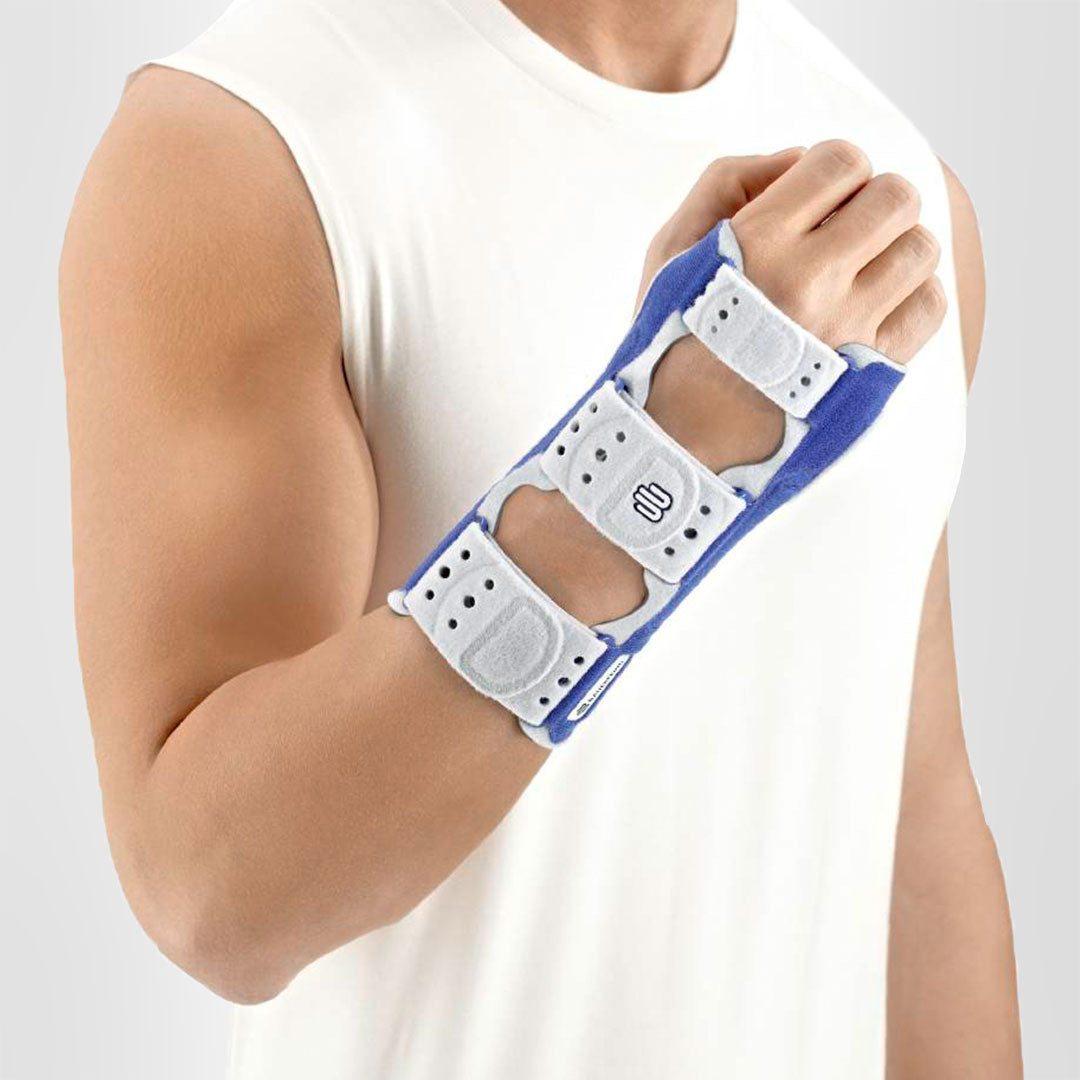
The ManuLoc wrist brace, with its lightweight splint stays and anatomic contour, stabilises the wrist and relieves pressure on the median nerves. This allows the soft tissue to heal and significantly reduces swelling. The brace effectively immobilises the joint and prevents further irritation of the inflamed or damaged tissue.
The ManuLoc is designed to be particularly comfortable during physiotherapy, increasing the effectiveness of any therapy and fitting into any treatment plan. The brace can be easily removed and put back on, even with one hand, and still allows full movement of the fingers and thumb. Its breathable and comfortable material makes it perfect for everyday use.
In most cases, the ManuTrain Wrist support would provide adequate pain relief. If you have severe symptoms and require the brace to minimise movement, we recommend the ManuLoc.