Some patients can develop a tendency to form clots (thrombosis) in the veins. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) occurs most commonly in the leg and can constrict or even close the blood vessels completely.
It is a very serious condition that carries a significant life-threatening risk of complications, such as the possibility of a pulmonary embolism. Immediate medical attention is highly recommended to prevent the long-term risks of the condition.
Causes of Deep Vein Thrombosis
There are several factors that can lead to restricted blood flow and cause venous thrombosis. Some of the most commonly known causes include:
Blood clots occur in the blood vessels. They are more common in the veins, but there is a slight possibility of clotting in the arteries.
Sitting or standing for long periods of the day. People who work long hours at a desk or who are constantly on their feet are more vulnerable.
Long periods of immobilisation and confinement to the bed, for example after a surgery, can lead to congestion in the leg veins.
- Inflammation in the legs
- Injury or trauma to the legs
- Changes in the bloodstream cause an increased platelet count. With time, these platelets become attached to the inner walls of the vein and tend to clump together, creating blockages.
Risk Factors of DVT
- Associated blood clotting disorders
- Presence of Varicose Veins
- Being overweight or obese, and a general lack of exercise or physical activity.
- Pregnancy in women
- Alcohol and Nicotine consumption
- Certain types of cancers
- Hormonal Contraceptives, i.e. “the pill”.
Typically, a combination of the above factors leads to venous thrombosis and can have a debilitating impact on the patient’s quality of life.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Symptoms
One of the most challenging aspects of deep vein thrombosis is the lack of symptoms in its initial stages.
Often referred to as a silent killer, a diagnosis can typically be delayed. With time as the disease progresses, there are several symptoms that appear, including:
- A “pull” feeling and a cramp-like pain are pretty standard.
- Feeling of heaviness and tension in the affected leg.
- Sensation of radiating heat around the ankle and lower leg.
- Bluish-red colouration on the skin.
- Associated clotting in the shin as chronic thrombosis kicks in.
It is difficult to diagnose deep vein thrombosis, which often results in delayed treatment. When the first symptoms of pain and discomfort appear, immediate medical attention is highly recommended.
In some cases, the thrombus (clot) detaches from the vein wall and can be carried through the body within the bloodstream. There are real risks of the clot reaching the lungs or the heart and blocking critical life-sustaining functions of these organs.
For example, a pulmonary embolism can lead to overload of the heart and eventually a cardiac arrest. Pulmonary embolism occurs in about 10-30% of all cases of deep vein thrombosis.
Diagnosis of Deep Vein Thrombosis
A complete medical history and physical examination allows doctors to understand the risk factors involved. Physicians rely on sophisticated imaging technology like Ultrasound and CT scans to locate and get a clear picture of the progression of the condition. A timely diagnosis can be instrumental in a swift and effective prognosis and is highly recommended.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Prevention
Lifestyle Changes
- Regular exercise, like jogging or walking, helps keep the veins in motion and ensures optimal blood circulation.
- Regular breaks during long work hours to stretch can help boost blood circulation and prevent the chances of developing a clot.
- Drinking enough water and a well-balanced diet can help regulate blood circulation and help with weight loss.
- Changes in lifestyle habits like drinking or smoking can help tremendously as a preventative measure.
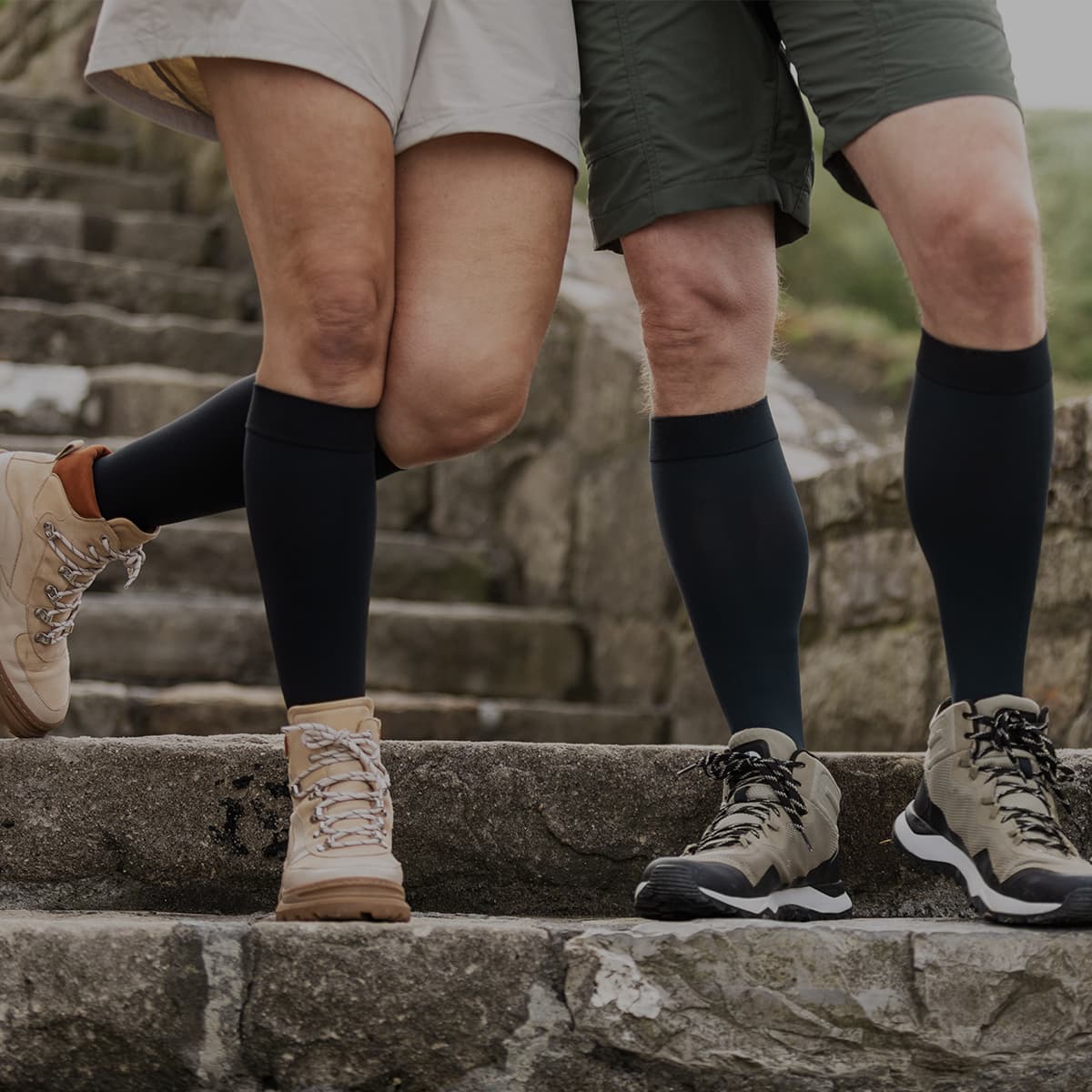
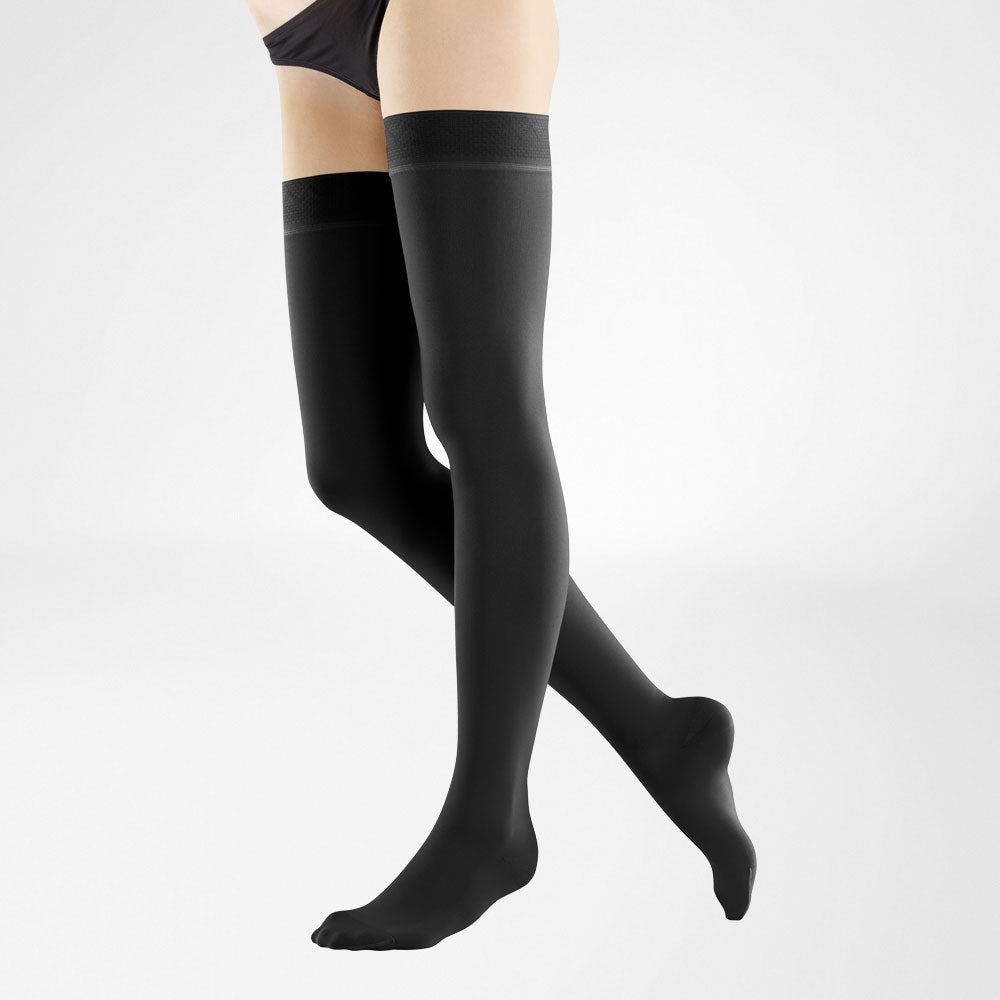
Medical Compression Stockings
Compression stockings can help prevent deep vein thrombosis. The medical-grade compression helps boost blood circulation by applying external pressure. The compression also supports the veins in the legs and can help prevent the formation of clots.
Treatment for Deep Vein Thrombosis
Treatment for deep vein thrombosis helps alleviate the symptoms by breaking down existing blood clots.
Prescribed Drug Therapy
If the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor will administer a drug that dissolves the blood clot (thrombolytic agent). This treatment lasts several days to a week and can, in many cases, also be done on an outpatient basis without hospitalisation.
Anticoagulant drugs are then given to prevent another blood clot.
Patients experiencing pain and inflammation in the legs are also advised to seek prescribed anti-inflammatory and pain medication like Ibuprofen or Panadol. However, long-term use of painkillers can have an impact on the health and quality of life of the patient.
Compression Stockings
VenoTrain Micro Compression Stockings
Medical compression stockings are helpful for both preventative and treatment measures for deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
VenoTrain Micro Compression Stockings apply compression and pressure to the surface of the legs, increasing blood flow and lowering the likelihood of a clot. The stockings also offer stability and support to weak blood vessel walls (Varicose Veins).
The breathable, skin-friendly microfibre fabric is designed for everyday use. Bauerfeind stockings come in many fashionable colours, such as regular tights, for wearing to work. Regular use of compression stockings can significantly improve the patient’s quality of life and shield them from the risk of venous thrombosis.
Bauerfeind has a range of compression garments suitable for all-day wear. These garments offer therapeutic benefits and aesthetically appear nicer than traditional-looking 'hospital socks'. This includes the VenoTrain Cocoon.
- With integrated cocoon skincare fibres made from cellulose, cotton, and a lipid skincare complex to ensure your skin stays moisturised and minimises the dry, itchy sensation.
- Class 2 compression
- Comfort heel and wide supportive band for dynamic, all-round comfort