Varicose veins result from a medical condition called Chronic Venous Insufficiency, or CVI. The impacted veins are swollen, enlarged, and twisted, and they have a blue or purple appearance.
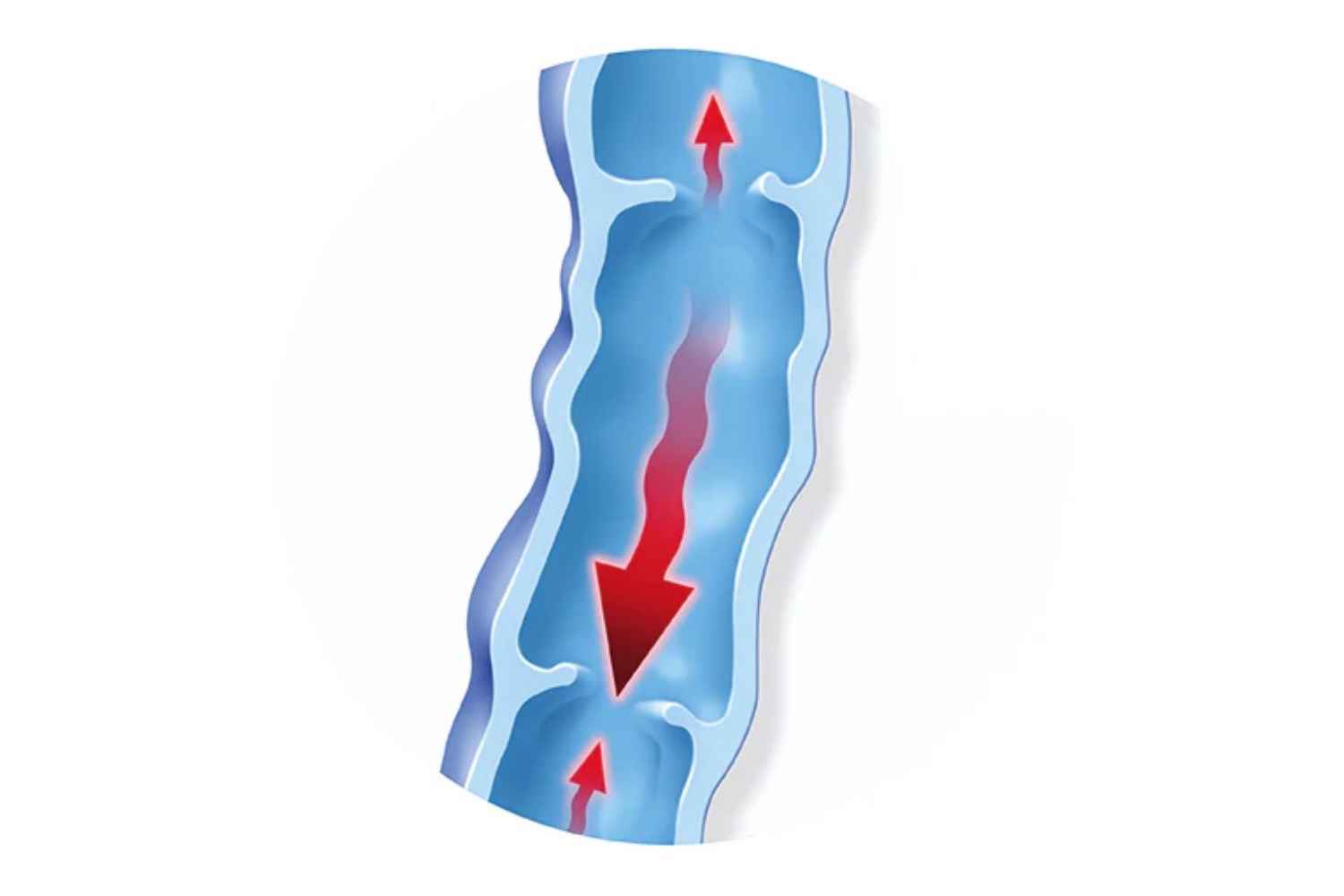
Our veins are primarily responsible for transporting deoxygenated blood from different parts of the body to the heart. Healthy veins pump blood against the pull of gravity; however, weak valves in the veins can lead to blood pooling in the lower legs.
In mild cases of varicose veins, the patient develops enlarged veins that appear as blue rope-like structures in the legs and ankles. There is some discomfort and swelling in the affected limbs.
In chronic cases, there are significant risks of degeneration of the veins, which can lead to open ulcers and, in the worst-case scenario, even a life-threatening embolism.
Causes of Varicose Veins
Various factors lead to an increased risk of developing Varicose Veins. Some of the most commonly known risk factors include:
- Some patients can inherit certain genetic predispositions that put them at an increased risk of developing varicose veins.
- Congenital weakness of the connective tissue.
- Older people are at an increased risk.
- Certain diseases, like deep leg vein thrombosis, result in blood clots that can compromise the veins and lead to Varicose Veins.
- Weakness of the heart, specifically the right side of the heart, can lead to a build-up of blood in the veins due to reduced heartbeat.
- Lifestyle choices like smoking and consuming alcohol.
- Lack of exercise.
- Being overweight or obese.
- Prolonged hours standing or sitting for long periods of time during work.
- Constricting clothing and shoes with high heels.
Varicose Veins Symptoms
Varicose veins are generally quite recognisable. The enlarged size and the blue swollen veins can be clearly seen through the skin. The veins arise due to sagging of the vein valves, causing the affected veins to swell up and expand. Some of the typical symptoms of varicose veins are:
- Heavy and tired legs.
- Feeling of tension in the legs, especially prominent during warm weather.
- Nocturnal cramps (nighttime) in the calf or foot.
- Increased water retention in the legs and ankles, leading to significant swelling and water retention (Edema).
- Burning or pain in the legs.
- Warm sensation and an itchy feeling in the legs.
Chronic Varicose Veins
If varicose veins are left untreated or neglected, the condition can progress and lead to long-term degeneration. The backflow and pooling of blood in the veins are a significant burden on the vascular system and increase the risk of blood clots (thrombosis).
In advanced patients, ulcers can develop in the lower legs, sometimes referred to as an open leg. Excessive clotting can wholly or partially clog a vein, referred to as venous thrombosis.
There are significant risks of thrombosis. Fragments can get dislodged from the veins and travel through the blood vessels through the heart into the lungs.
This creates a life-threatening vascular blockage called a pulmonary embolism and can be lethal. A prompt diagnosis is highly recommended for an effective treatment path.
Diagnosis of Varicose Veins
A complete patient history and physical examination can allow a professional medical practitioner to gather key insight into the risk factors involved and the progression of the condition.
An examination is necessary to determine whether it is primary or secondary varicosis. It is also necessary to clarify whether deep leg veins are affected or if other potential conditions, such as kidney or heart disease, may cause water to build up in the legs.
Sophisticated imaging technology, such as Ultrasound, can be used to gain valuable information about the progression of the condition and whether there are any associated long-term risks.
Treatment For Varicose Veins
Treatment for varicose veins depends on the severity. A physician focuses on relieving a patient’s symptoms and taking measures to slow and sometimes halt the progression of long-term degeneration. Some of the most effective measures include:
Changes in Lifestyle
It is highly recommended that patients consider weight loss. Reducing overall body weight can reduce the stress on the lower legs and thus relieve the blood vessels.
Making sure to take enough breaks to stretch between long hours of standing can help stretch the muscles and provide some relief from daily stress.
Making small lifestyle changes, such as using stairs whenever possible, can help train the leg muscles of those with busy work lives.
Rehabilitation and Physiotherapy
- Regulated physiotherapy helps with targeted muscle training.
- The exercises can help promote the reorganisation of the muscles.
- A strong calf muscle helps reinforce the lower legs and supports the push of blood towards the heart against the pull of gravity.
- Regular exercises, yoga, jogging and walking can be effectively incorporated into daily life.
Prescribed Medication
In cases of inflammation in the legs, anti-inflammatory medication may be recommended to improve the patient’s quality of life.
If a patient experiences pain, medication like Ibuprofen and Panadol can be used to manage symptoms.
Drug therapy can prevent thrombosis. For example, ointments with hirudin have anticoagulant effects and can prevent the formation of clots.
Lymphatic Drainage Massage
Lymphatic drainage massage should stimulate the surrounding area and naturally encourage the drainage of lymph fluid to alleviate symptoms. In chronic cases, more invasive methods of lymph drainage might be necessary.
Compression Therapy
Compression therapy is the gentle application of pressure on the affected area using a medical compression bandage.
Compression stockings like the VenoTrain range can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life. Regular use of a compression bandage is instrumental in preventing the progression of Spider veins and varicose veins.
The compression helps encourage the flow of lymph fluid out of the affected legs and can significantly reduce swelling. It also acts as external reinforcement that helps provide enough pressure for the blood to flow normally.
Surgical Intervention
Patients can choose to go for a surgical approach to treating varicose veins. A vein specialist can perform:
- Radio wave therapy using microwave radiation.
- Sclerotherapy through chemical agents for smaller varicose veins and through laser for more advanced cases.
- Surgical removal of the affected vein by stripping or other surgical procedures; however, research shows that this method has a higher risk of recurrence.
Surgical options can alleviate symptoms and provide relief to the affected limbs in a relatively quick period of time.
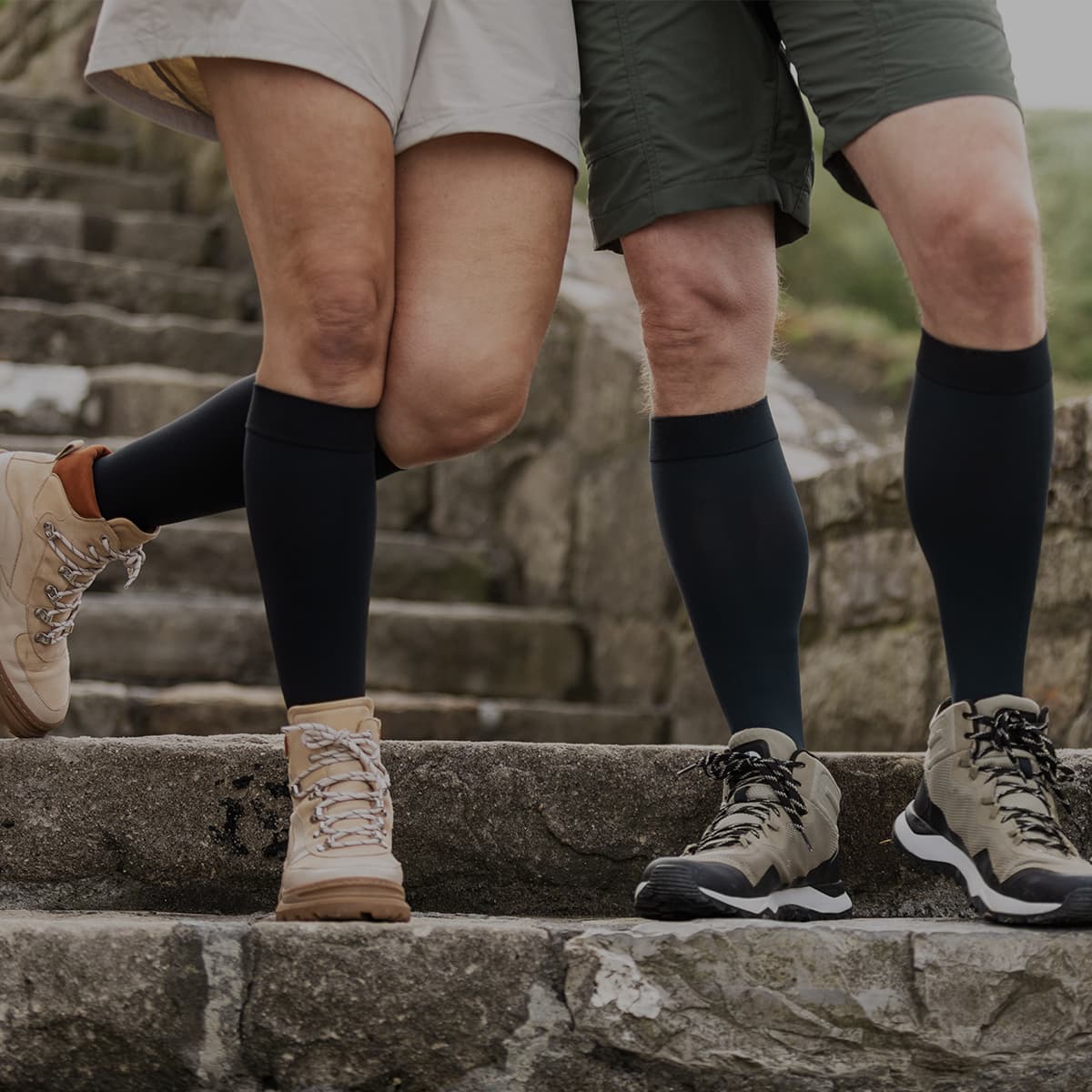
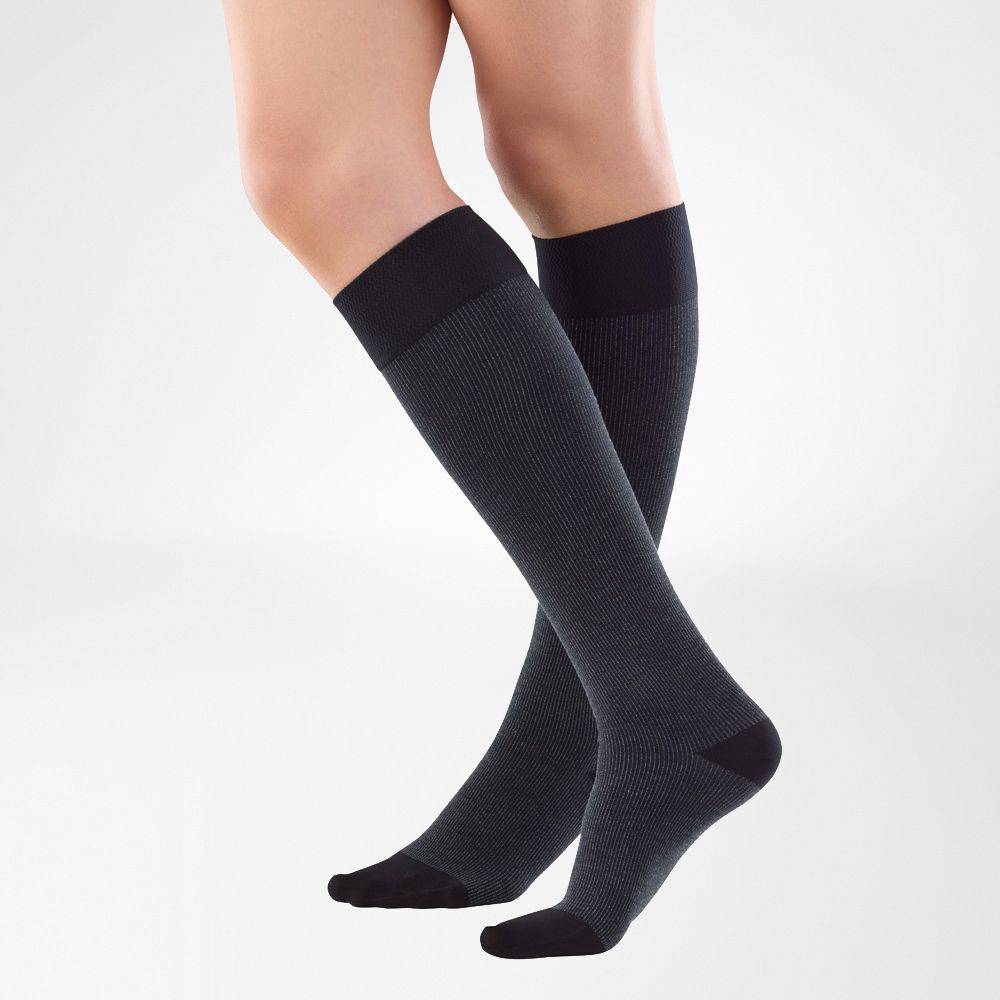
Compression Stockings For Varicose Veins
VenoTrain Micro Compression Stockings
Medical-grade compression stockings are used for varicose vein therapy to prevent the disease from accelerating, stabilise the affected veins, and better stimulate blood flow.
They are also an important part of therapy in the post-treatment period after the vein surgery mentioned above. In addition, compression stockings have proven to be extremely valuable in preventing varicose veins and leg vein thrombosis. Pressure is exerted on the vein, allowing the vein wall to withstand the internal pressure more easily, and the venous valves to close again. This prevents the formation of further sags.
In addition, compression stockings promote the return flow of blood to the heart and thus reduce the risk of thrombosis.
High-quality compression stockings, such as the VenoTrain range, distribute the pressure consistently over the entire surface of the leg.
This, coupled with the skin-friendly materials, offers a high level of comfort and therapeutic benefit. The stockings are available in a series size or made to measure, knee or thigh stockings, and tights in different colours. As a result, they can be combined very well with everyday clothing and simply look like everyday stockings or socks.
The VenoTrain Cocoon is a medical compression stocking with integrated skincare fibres. Lipophilic substances are applied to the skin while wearing the stocking, particularly protecting dry and sensitive skin. It protects the wearer against dryness, scaliness and itching.