What is Supination Trauma?
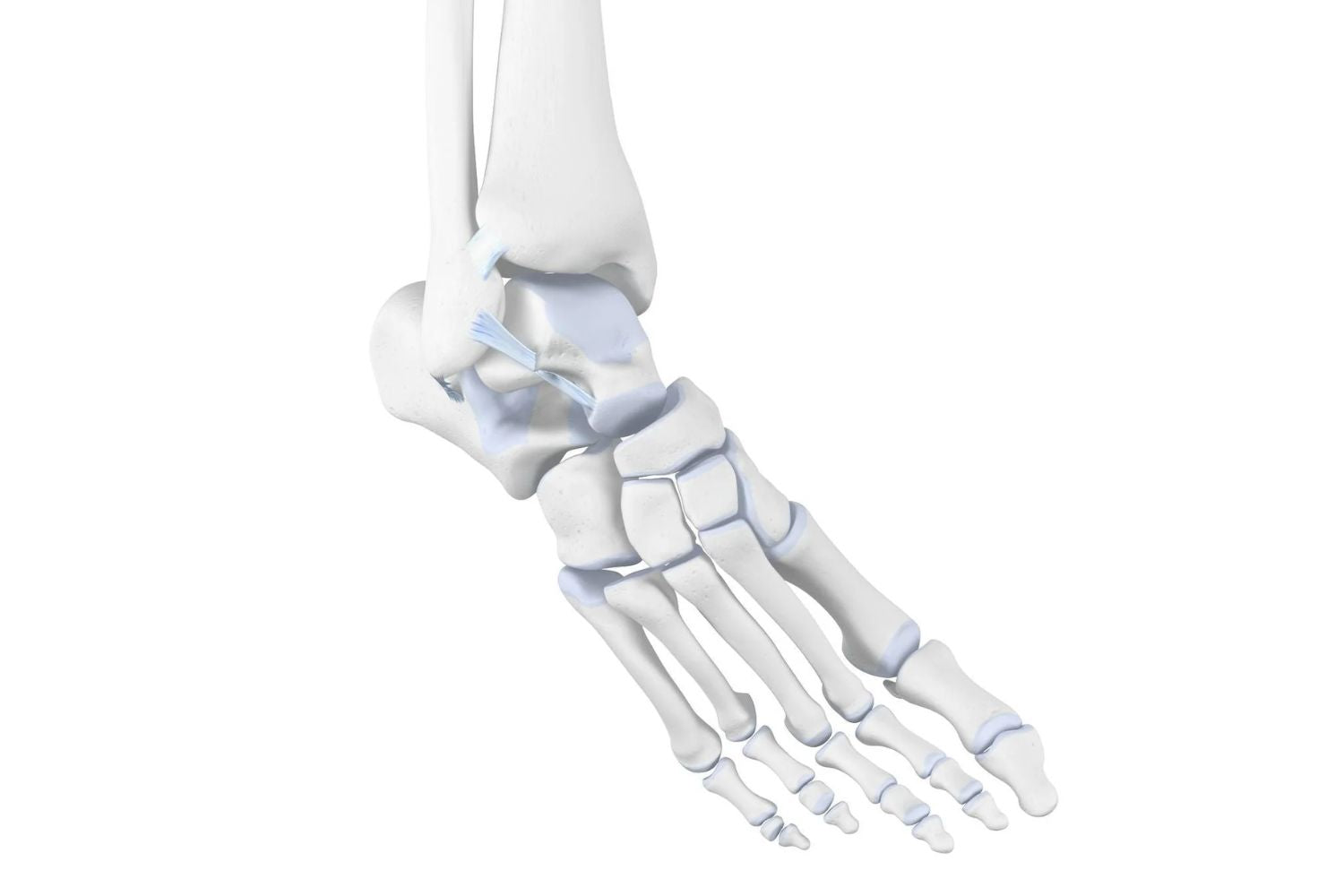
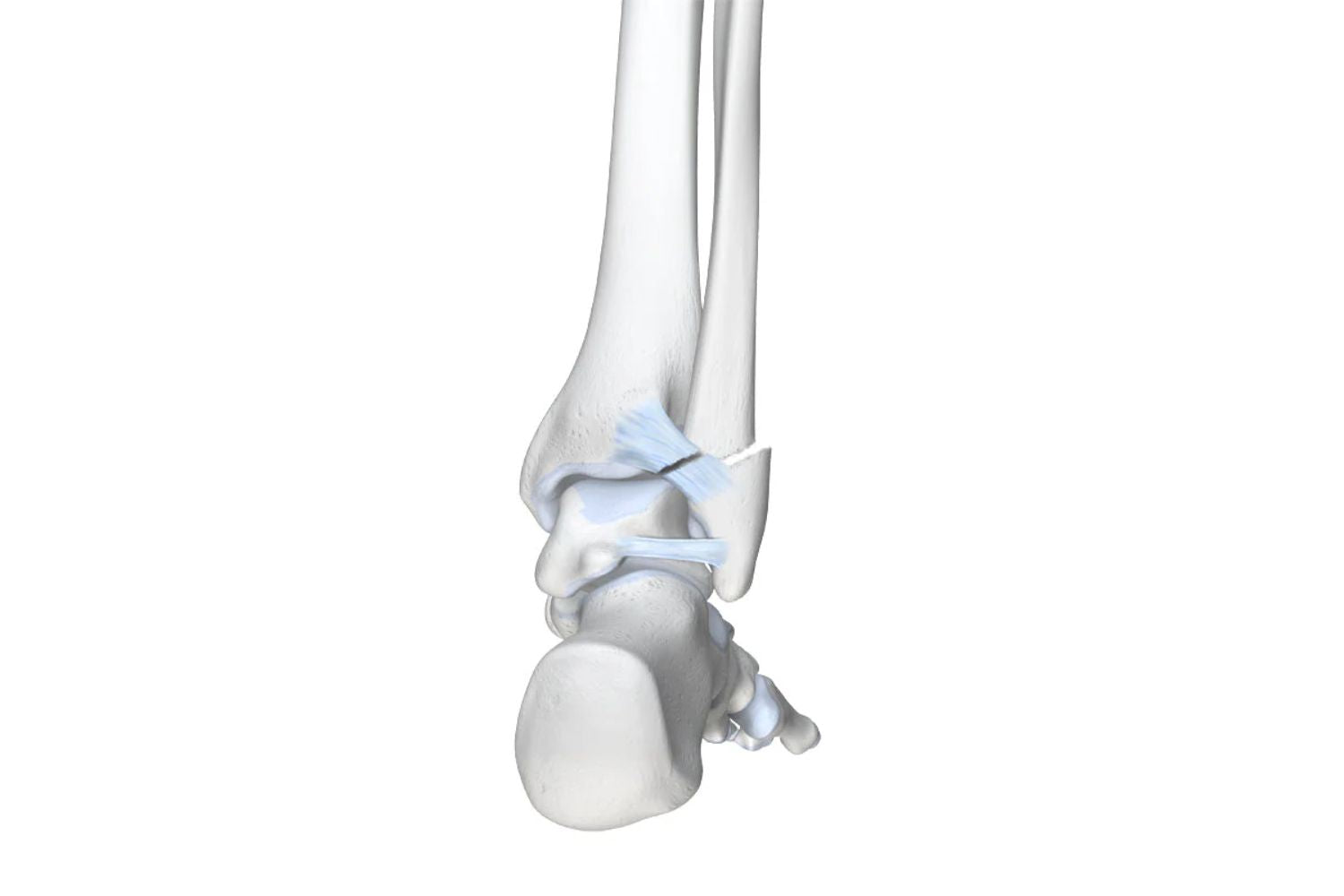
The ankle consists of two parts: the upper and lower ankle. The upper ankle has several ligaments that stabilise the joint and allow for movements such as walking, jumping, and other sporting activities.
The ligaments are elastic, i.e., they stretch within a limit to allow for short-term expansion of joints (stretching). In supination trauma, ligaments have been excessively stretched due to abnormal amounts of stress. Bending the foot inwards can overload the ligaments, leading to severe pain and restricted joint mobility.
Supination Vs. Pronation
“Supination” (Latin for bent position) describes the movement of the foot inwards, while “trauma” refers to the injury caused by forces that result in an abnormal and often violent movement.
More specifically, a supination trauma refers to an injury caused by excessive bending over the outer edge of the foot. The movement pushes the bone inwards over the edge of the foot. In contrast to supination, pronation trauma involves the movement over the inner edge.
Both foot pronation and supination injuries can be varying degrees of severity, depending on how damaged the joint and surrounding areas are. The damage can range from a ligament stretch or tear to serious complications.
Following a supination trauma, the patient may also experience bruising and edema around the ankle joint. In the worst cases, the sensitive joint capsule might be affected and would require special treatment.
How to Diagnose Supination Trauma
Ankle injuries are relatively common and should be addressed with due importance. Diagnosing the extent of the injury to determine complications is crucial for a well-guided recovery.
Imaging examinations like MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) or CT scans (computed tomography) are often used to better understand the extent of the injury (Ligament stretch vs. ligament tear).
Symptoms of Foot Supination
Even in mild cases, the site of the injury is often very painful and, in most cases, severely limits the daily functionality of the ankle joint. Patients suffering from this condition experience sharp pain under strain as a recurring symptom until treated.
Risk and Complications of Supination Trauma
A supination trauma has associated risks and complications. For example, blood vessels in the joint might get damaged, causing bleeding, turning the foot “blue”. In severe cases, edema may cause pressure to be applied to the vessels and nerves, which can lead to a numbing sensation in the foot.
If proper diagnosis and treatment are avoided, there are significant long-term risks. Ankle injuries, both minor and serious, could lead to chronic symptoms like osteoarthritis (excessive joint wear) if left untreated. It is imperative that professional medical treatment is sought immediately to avoid degeneration of the ankle joint.
Treatment of the Supination of the Foot
Contrary to the severity of the injury, most treatments involve conservative approaches, i.e. non-surgical.
First Aid
Immediate first aid measures are highly recommended after a supination trauma. A good guideline to follow is the RICE rule:
- Rest: The injured joint should be immobilised immediately. Rest should be prioritised, and no stress should be applied to the joint.
- Ice: Cooling the joint is recommended. To prevent and minimise swelling, an ice pack, wrapped in a cloth, should be applied immediately after injury.
- Compression: Compression bandages and medical ankle braces can help relieve pain and reduce swelling. These provide support and prevent excessive stress and movement of the ankle joint.
- Elevation: Elevation of the injured foot above heart level, preferably mounted, prevents further complications by managing and preventing edema.
- Prescribed Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation
- Anti-inflammatory and pain medication can help alleviate the pain and discomfort caused by supination trauma.
- Prescribed rehabilitation exercises, which can strengthen the joint and provide more stability to the ligaments, are highly recommended.
- Remedial massage and hydrotherapy can also be instrumental in managing the associated symptoms of edema. Physiotherapy is very beneficial during the recovery process as it helps to boost blood circulation and develop ankle stability.
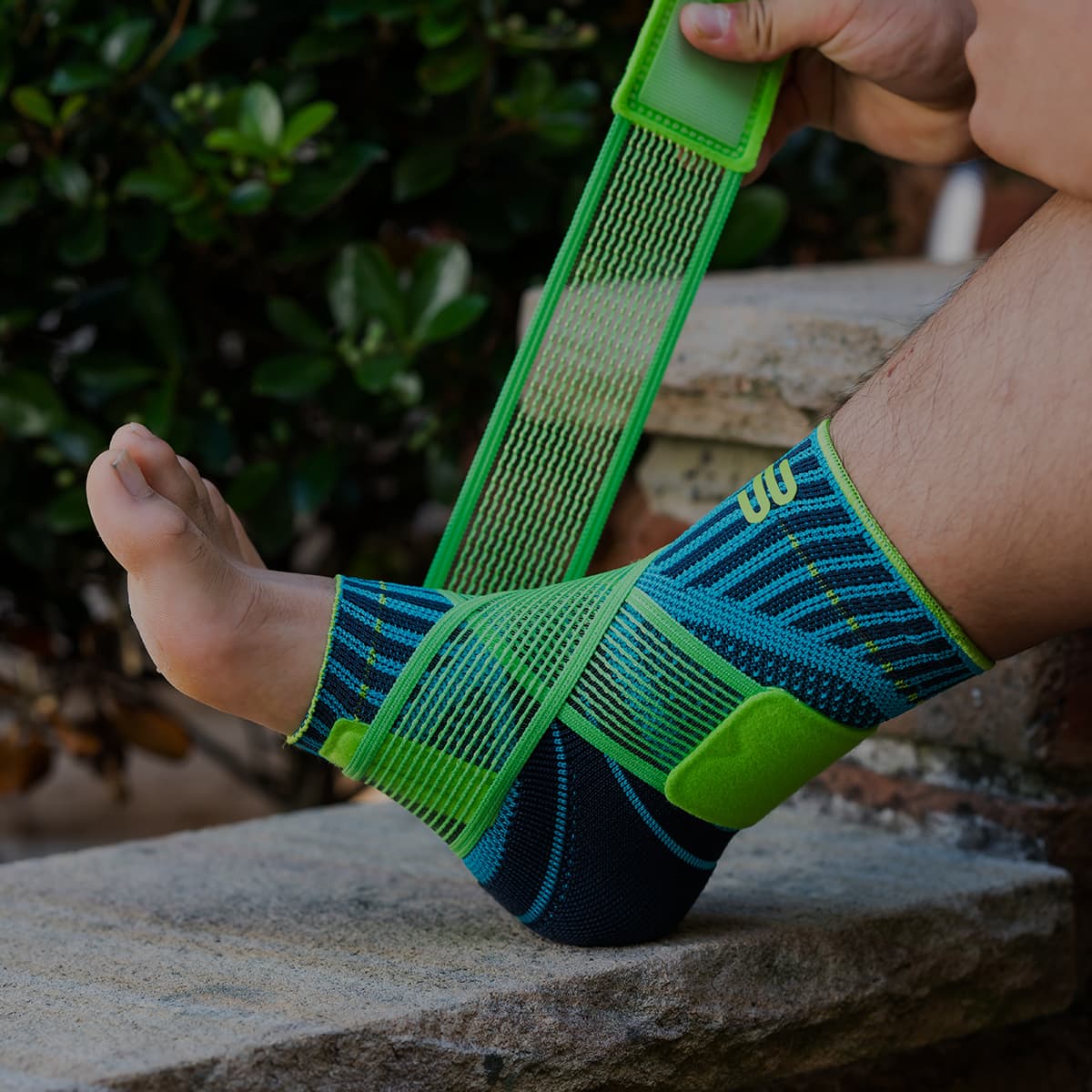
Medical Ankle Braces
Ankle braces and orthoses play a significant role in a smooth and effective recovery following a supination trauma. After being injured, the ankle is more susceptible to further or re-injury.
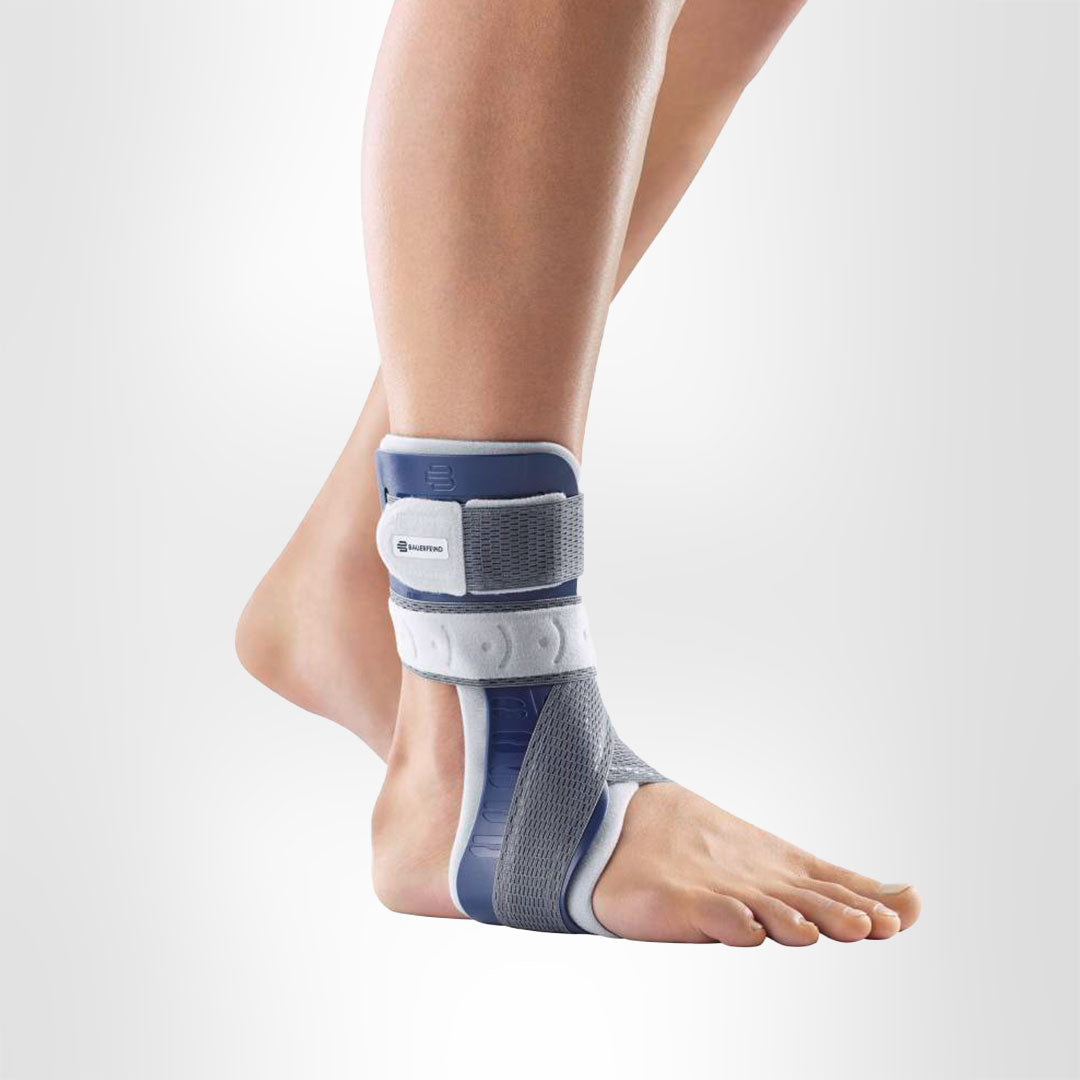
Wearing a Bauerfeind ankle brace, like the MalleoLoc L and the MalleoLoc L3, can minimise the chances of further injury by providing enhanced stability, proprioception and medical-grade compression.
Surgical Intervention
Contrary to belief, surgical paths of treatment are only necessary in complicated cases. In cases of torn ligaments, there could be internal complications like bone fragments created due to injury. This would necessitate surgery for a full recovery.
Prevention of Foot Supination
Trauma to the ankle joint is very painful and can be debilitating to an individual’s day-to-day activities. Generally, most cases of supination trauma result from unfortunate, abnormal movements of the foot. Some fast-paced movements in sports, especially involving rapid changes in direction in football or basketball, carry an inherent risk that leads to supination of the foot.
Running shoes for Supination of Foot
Wearing good-quality training shoes is recommended as they also provide ample support to the ankle. Improving proprioception (awareness of the body’s position and movement) is one of the most effective measures in preventing supination trauma.
Exercise for Supination of the Foot
Training to be more conscious of one’s movements is a formidable tool that helps patients learn to coordinate movements and react to rapid changes better. Small everyday solutions would include sandals and running shoes for supination, supportive gear like ankle braces, or supine core exercises to build resilience. Wearing a Bauerfeind ankle brace can minimise your chances of injury by providing enhanced stability, proprioception, and medical-grade compression.
Ankle Brace to Prevent and Treat Supination of the Foot
MalleoLoc L Ankle Brace
As a supination injury is usually painful, ankle braces are very beneficial during the treatment process. Bauerfeind’s MalleoLoc L and MalleoLoc L3 ankle braces provide additional support and stability to the joint.
The MalleoLoc L and MalleoLoc L3 are geared explicitly for supination trauma and provide crucial support to the ankle while walking fast or on uneven ground, climbing stairs or performing light sporting activities such as hiking or cycling.
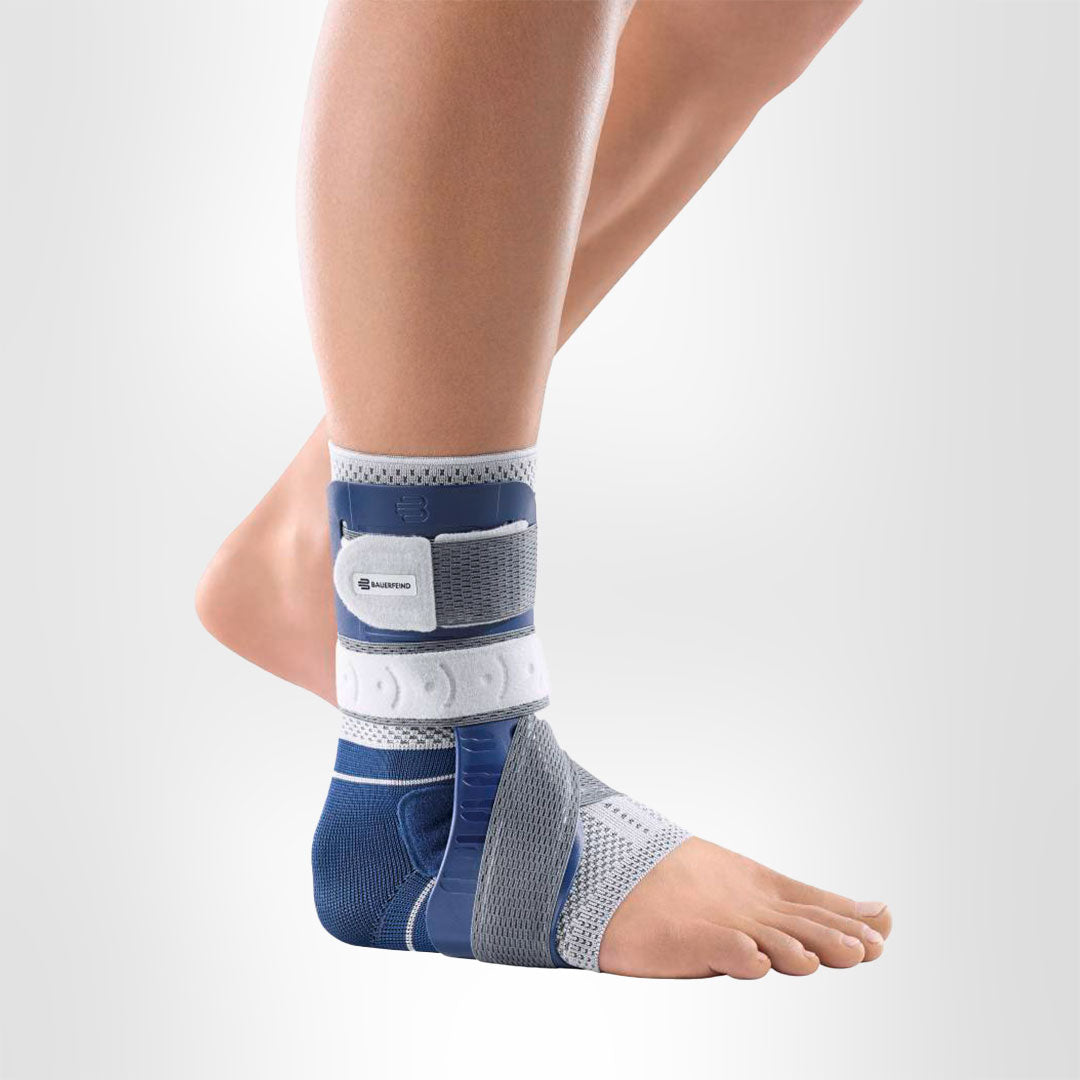
Both the MalleoLoc L and MalleoLoc L3 ankle braces feature an anatomically shaped L-shell, which runs along the front of the outer side of the ankle. This shell provides extra stability to the foot laterally, preventing further or re-injury.
Additionally, the MalleoLoc L3 ankle brace features flat-knit, elastic, and breathable fabric that delivers medical-grade compression, helping to reduce edema and promote circulation around the ankle joint.